Wireman Training
About department
description
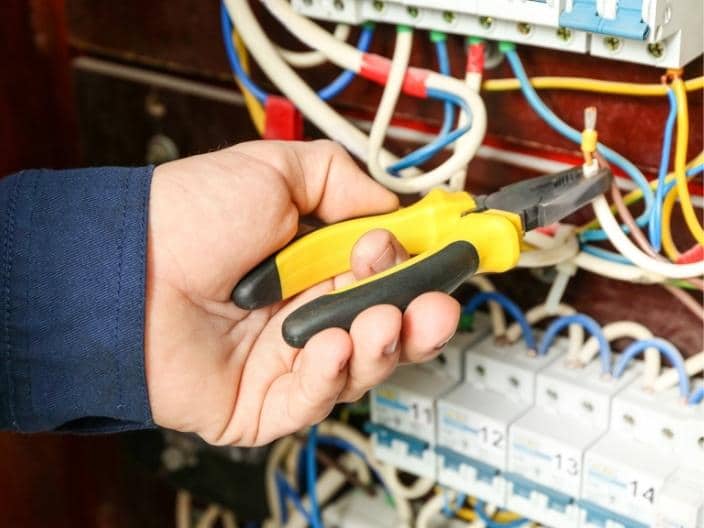
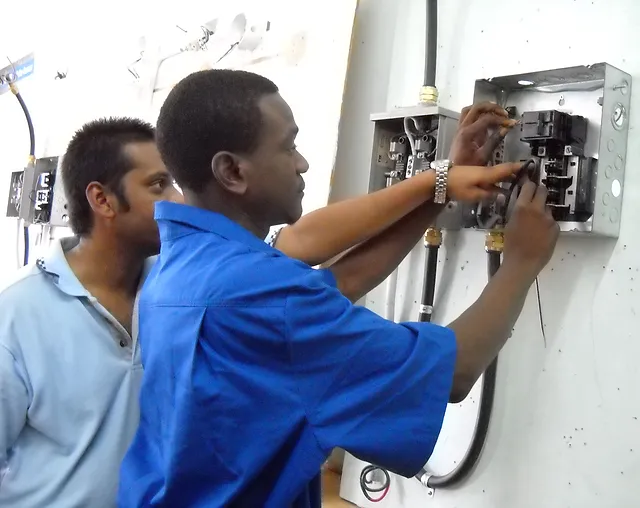
Wireman is an electrical engineering vocational trade. The syllabus for trade mainly comprises topics like how to repair and replace wiring and electrical systems in houses and factories; prepare the grounding system and connect wiring to the structure; install wiring, security and fire-protection systems; install lighting fixtures and troubleshoot electrical systems; read a variety of meters to check current values and the amount of current being sent or received and the like others. Trade is good from job point of view and self-employment as it opens many opportunities in various fields.

Connect with us
Benificial
- Courses under this: Training may include:
- Electrical Safety Procedures
- Wiring Installation Techniques
- Electrical System Troubleshooting
- Reading Electrical Diagrams and Blueprints
- Grounding and Bonding Systems
- Installation of Lighting Fixtures
- Fire Protection Systems
- Security Systems Installation
- Use of Electrical Testing Equipment
- Codes and Regulations Compliance
- Course Level: It’s usually a vocational training program.
- Duration: The duration can vary, but it typically ranges from six months to two years, depending on the program’s intensity and depth.
- Mode: Offered in various modes including full-time, part-time, and apprenticeship programs. Some institutions may also offer online or distance learning options.
- Eligibility Criteria: The eligibility criteria may vary depending on the institution and program. Generally, candidates should have completed at least secondary education (10th grade or equivalent) from a recognized board. Some programs may have specific age criteria or prerequisites related to technical aptitude.
- Admission Process: Admission processes may involve submitting an application form along with academic transcripts, attending an entrance exam or interview, and meeting any other requirements set by the institution.
- Areas of Employment: Graduates of Wireman courses can find employment opportunities in various sectors, including:
- Construction industry
- Electrical contracting firms
- Manufacturing companies
- Maintenance departments of commercial buildings and factories
- Government agencies
- Self-employment as independent contractors or entrepreneurs in electrical contracting or maintenance services.
- Courses under this: Training may include:
- Electrical Safety Procedures
- Wiring Installation Techniques
- Electrical System Troubleshooting
- Reading Electrical Diagrams and Blueprints
- Grounding and Bonding Systems
- Installation of Lighting Fixtures
- Fire Protection Systems
- Security Systems Installation
- Use of Electrical Testing Equipment
- Codes and Regulations Compliance
- Course Level: It’s usually a vocational training program.
- Duration: The duration can vary, but it typically ranges from six months to two years, depending on the program’s intensity and depth.
- Mode: Offered in various modes including full-time, part-time, and apprenticeship programs. Some institutions may also offer online or distance learning options.
- Eligibility Criteria: The eligibility criteria may vary depending on the institution and program. Generally, candidates should have completed at least secondary education (10th grade or equivalent) from a recognized board. Some programs may have specific age criteria or prerequisites related to technical aptitude.
- Admission Process: Admission processes may involve submitting an application form along with academic transcripts, attending an entrance exam or interview, and meeting any other requirements set by the institution.
- Areas of Employment: Graduates of Wireman courses can find employment opportunities in various sectors, including:
- Construction industry
- Electrical contracting firms
- Manufacturing companies
- Maintenance departments of commercial buildings and factories
- Government agencies
- Self-employment as independent contractors or entrepreneurs in electrical contracting or maintenance services.



